Many experts believe that chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease caused by infection, which may be accompanied by an autoimmune disease characterized by damage to the organ parenchyma and interstitial tissue.The medical community has known this disease since 1850, but even today, it is still very little known and difficult to treat.Chronic bacterial (6 - 10%) and non-bacterial (80 - 90%) prostatitis is the most common and socially significant inflammatory disease in men, significantly reducing their quality of life.The disease mainly occurs in young and middle-aged people, and often comorbid and reproductive dysfunction (sexual ability decline, infertility, etc.).Of the male cases between the ages of 20 and 40, 8% - 35% have the disease.
The cause of bacterial prostatitis is that suppurative bacteria penetrate the glands from the urethra or through lymphatic and hematopoiesis.The cause and pathogenesis of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis remains unclear.It mainly affects men over 50 years of age.
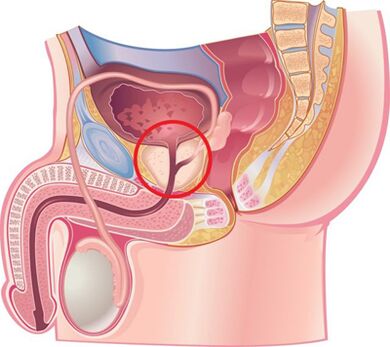
Causes of the disease
Chronic prostatitis is currently considered a multi-causal disease.It is believed that the disease occurs because of infection entering the prostate, and the pathological process then proceeds without the involvement of the prostate.Many non-communicable factors contribute to this.
Infectious factors for the development of chronic prostatitis
In 90% of cases, the pathogen penetrates iron from the urethra, thus acute or chronic prostatitis occurs.Note the asymptomatic vector.The course of the disease is affected by the protective state of the human body and the biological properties of the pathogen.It is assumed that the transition from acute prostatitis to chronic is the loss of tissue elasticity caused by excessive fibrous tissue products.
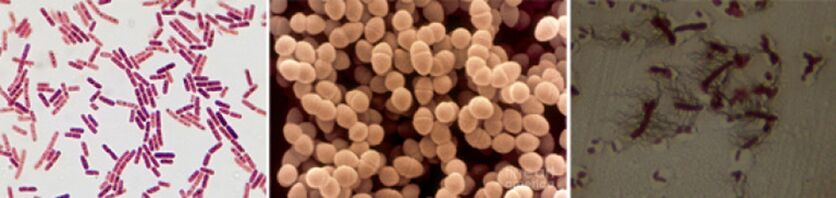
Among the causative agents of chronic prostatitis, the following pathogens are found:
- In 90% of cases, the disease reveals Gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), Enterococcus faecalis (Enterococcus faecalis), and less than - Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, klebsiella spp., proteus spp., proteus spp.Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter and Actobacterium spp.Camera-positive bacteria of enterococci, streptococci, and staphylococci are rare.
- Coagulant-negative staphylococci, urea mass, chlamydia, trichomonia, Gardnerell, anaerobic bacteria and fungi of the genus Candida have not been finally clarified.
Infections to the prostate penetrate in a variety of ways:
- The ascending path is most likely demonstrated by a combination of prostatitis and urethritis.
- Hematoma prostatitis occurs with the penetration of blood flow into the gland and occurs through chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, periodontitis, pneumonia, cholecystitis and cholangitis, purulent diseases of the skin, purulent diseases of the skin, etc.
- Contact chronic prostatitis suffers from urethritis and urethral stenosis when the infection is elevated with urine current and during diagnostic and therapeutic urological manipulation (catheter, irritating, irritating, irritating), including purulent infection of the kidney, purulent infection of the kidney, tubules, antidepressant and funiculite.
- Lymphological infections cause the prostate to penetrate the prostate, the thrombosomes of the hemorrhoid veins, and so on.
Non-infectious factors in the development of chronic prostatitis
Chemical factors
According to experts, the main role in the development of chronic prostatitis belongs to the intracorporeal reflux of urine, when urine is cast from the urethra into iron, which leads to the violation of the prostate and the emptying of the seminal vesicles.
Through disease, vascular responses develop into edema of the organs, nerve and body fluid regulation of urea smooth muscle tissue and activation of alpha are disturbed1- Adrenal receptors can lead to the development of dynamic obstruction and contribute to new intrathoracic reflux.
Urine containing refluxed urea can lead to the development of a "chemical inflammatory reaction".
hemodynamic disease
Supports chronic inflammation in circulatory disorders in the pelvis and scrotum.Arrest develops in the form of obesity, sexual withdrawal, libido disorders, frequent hypothermia, mental and physical overload, in the sedentary lifestyle of drivers, office workers, etc.Maintaining the inflammatory process, taking spicy food, alcohol and smoking, etc.
Other factors
There are many other factors that support the chronic inflammatory process in the prostate.These include:
- hormone.
- Biochemical.
- Violation of immune response.
- Autoimmune mechanism.
- Infectious and allergic processes.
- Characteristics of the structure of the prostate that lead to difficulties in complete drainage.
Often, it is impossible to establish the cause of chronic prostatitis.
Prostatitis classification
According to the classification proposed by the National Institutes of Health in 1995, prostatitis is divided into:
- Acuity (Class I).It is 5-10%.
- Chronic bacteria (Class II).It is 6-10%.
- Chronic nonbacterial inflammation (Class IIIA).It is 80-90%.
- Chronic nonbacterial noninflammatory (category IIIB) or chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
- Chronic prostatitis detected incidentally (category IV).
Signs and symptoms of chronic prostatitis
The process of chronic prostatitis is long, but it is not monotonous.Cycles of exacerbation are replaced by periods of relative rest that occur after comprehensive anti-inflammatory and antibacterial treatment.
The development of chronic bacterial prostatitis is usually preceded by bacterial or gonorrhea-based urethritis, non-bacterial - circulatory diseases in the pelvic organs and scrotum (hemorrhoids, genocytes, etc.).
Patients with chronic prostatitis present many complaints.They've been treated by doctors for years but rarely checked for prostate disease.About a quarter of the patients reported no complaints or had minimal clinical symptoms of the disease.
Complaints of patients with chronic prostatitis can be conditionally divided into several groups.
Interference with urination related to urethral narrowing:
- Having difficulty initiating urination.
- The urine is weak.
- Intermittent or urination drops.
- A feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Symptoms due to irritation of nerve endings:
- Frequent urination.
- The call to urinate is keen and strong.
- Small portion of urination.
- Urinary incontinence during the urge to urinate.
Pain syndrome:
- Pain varies in intensity and nature.
- Pain positioning: lower abdomen, perineum, rectum, groin and lower back, inner thighs.
Sexual dysfunction:
- Pain in rectal and urethra during ejaculation.
- Slow erection.
- Loss of orgasm.
- Premature ejaculation, etc.
From a nervous system perspective: Neurotics focus on their own health.
Signs and symptoms of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) in men has common symptoms of chronic prostatitis, but there are no bacteria in the third part of urine and prostate secretions at the time of examination.Chronic nonbacterial interstitial cystitis, rectal disease, pelvic floor spasmodic myalgia syndrome and functional prostate lesions caused by organ innervation and its hemodynamic disorders can simulate CPPS.
If autonomic function is impaired, weakness and disruption of glandular innervation is observed, which is manifested by difficulty in rapid and complete closure of the urethral lumen.In this case, urine continues to be discharged drop by drop for a long time after urination.In such patients, studies reveal increased instability and excitability, manifested by increased sweating and excitability of cardiac activity as well as changes in dermatography.
complications of disease
Chronic prostatitis has a long course and is accompanied by sexual and reproductive dysfunction, the development of diseases such as seminal vesiculitis and epididymitis, and organ sclerosis.Organ sclerosis worsens local microcirculation and urodynamics, as well as the outcome of surgical intervention.Fibrosis of the tissues surrounding the urethra leads to the development of urinary disorders.
diagnosis
Because chronic prostatitis can occur for a variety of reasons, it needs to be diagnosed using a battery of diagnostic tests.The success of treatment depends on the correct identification of the cause of the disease.The diagnosis of chronic prostatitis is based on the following data:
- Typical triad of symptoms.
- Complex physical approach (digital rectal examination of the prostate).
- A set of laboratory methods (urinary analysis and microscopy of prostate secretions, culture and determination of microbiota sensitivity to antibacterial drugs, general analysis of urine and blood).
- To detect gonococci, bacterioscopy, PCR, and serological methods (for detection of Ureaplasma and Chlamydia) on urethral smears are required.
- Urine fluorometry.
- Prostate biopsy.
- A set of instrumental methods (ultrasonography).
- Determine the patient's immune status.
- Determine the status of the nervous system.
- Due to inability to treat and suspected development of complications, calculations and magnetic resonance imaging, seeding, etc.
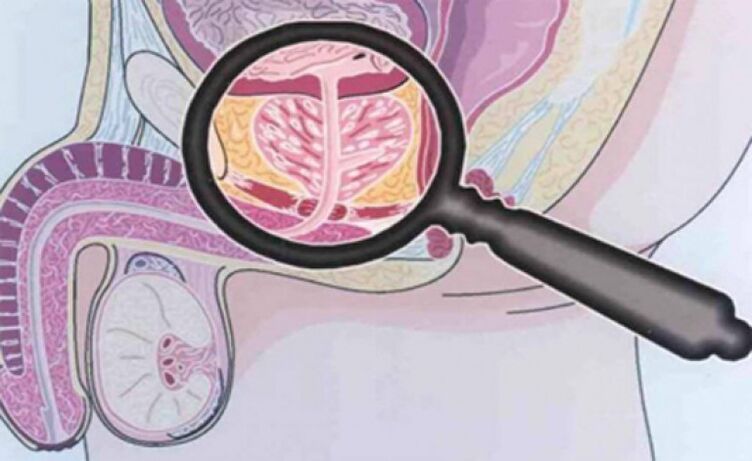
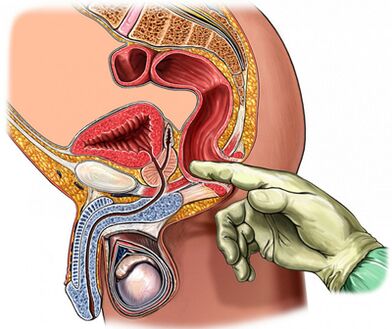
Palpate the prostate
Palpation of the prostate, which increases and decreases during the aggravation period during the subsidiary of the inflammatory process, is crucial in the diagnosis of the disease.In chronic prostatitis, iron swells and pain during the period of exacerbation of iron.
The density of organ consistency may vary: palpate the softening and compacting areas, identifying the western region.During palpation, the shape of the gland, the condition of the seed nodules and surrounding tissue can be evaluated.
The process of transrectal digital examination is combined with epileptic seizures of the gland.Sometimes it is necessary to obtain secrets from each share separately.
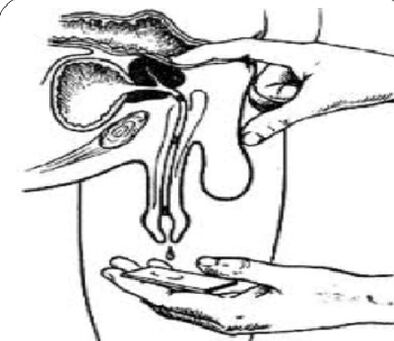
Analyze the secrets of 3 cups of urine and prostate
The gold standard for the diagnosis of chronic prostatitis is:
- Collect the first part of the urine.
- Collect the second part of urine.
- Get the secret of the glands through massage.
- Collect the third urine fraction.
Next, microscopic and bacteriological examinations were performed on the material.
Inflammation of the prostate:
- Number of microorganisms (CFU) exceeds 103/ml (104/ml for Staphylococcus epidermis), but should not be ignored by dozens and hundreds of calculated few microorganisms.
- The presence of 10-15 leukocytes in a field of view detected by a microscope is the accepted criterion for the presence of an inflammatory process.
The secret to the third part of the prostate and urine is subject to microscopic and bacteriological studies:
- In chronic bacterial prostatitis, an increase in the number of white blood cells in the urine of the secretions of the glands and in the third urine is noted, releasing bacteria (mainly from the intestinal tract).
- Due to nonbacterial prostatitis, an increase in the number of white blood cells in the secret gland was noted, but no flora was detected.
- With CTB, the amount of white blood cells and bacterial flora did not increase.
Normal indicators of prostate secrets:
- There are less than 10 white blood cells in the visual field.
- Pebble particles are a big number.
- No microorganisms.
In the secret chronic prostatitis of the prostate, it is found:
- In the field of view, the number of white blood cells is 10-15.
- The amount of lecithin granules is reduced.
- The pH of secretion shifts to the alkaline side.
- The levels of acid phosphatase are reduced.
- Increased lysozyme activity.
Negative results of obtaining prostate secrets have proven lack of inflammatory processes.
The value of secret prostate testing remains.Often, during the crystallization process, a characteristic pattern is formed in the form of fern flakes.This pattern does not form a scenario in which changes in the androgenic background occur if the secret aggregation properties of the prostate are violated.
Ultrasound examination
If prostate disease is suspected, it is best to perform ultrasound on the gland itself (transrectal ultrasound), kidneys, and bladder, which allows us to determine:
- The volume and size of the gland.
- The existence of stone.
- The size of the seminal vesiculus.
- The condition of the bladder wall.
- Residual urine output.
- Structure of the scrotum.
- Another pathological type.
Other prostate examination methods
- Urodynamic status (study on urinary flow rate) can be easily and simply determined using studies such as urinary flow rate.With this study, signs of bladder outlet obstruction can be detected in a timely manner and dynamic monitoring can be carried out.
- A needle biopsy is performed if abscess formation, benign hyperplasia, and prostate cancer are suspected.
- To determine the cause of subvesical obstruction, X-rays and endoscopy are required.
- If the inflammation process is long, urethral cystoscopy is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
Chronic prostatitis should be associated with proinflammatory cysts, autonomous prostatitis, stagnant prostatitis, pelvic floor, psychological surgical disease, pseudodroplet-vein-reflex sympathetic dystrophy, other sexual symptoms, cysts, sexual behavioral diseases, sexual diseases, inflammatory diseases, sexual diseases, inflammatory diseases, terminology diseases, terminology, osteoplasmic diseases, obstetrics and gynecology, obstetrics and gynecology, terminology, terminology, terminology, terminology, women's symptoms, inflammatory diseases, inflammatory diseases, inflammatory diseases, inflammatory diseases.Disorders, sexual disorders, sexual dysfunction.Hypertrophy of the bladder neck, urethra stenosis, tuberculosis, prostate cancer and bladder, urethra disease, chronic ipipidimite, inguinal hernia.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Treatment of chronic prostatitis should start with changes in the patient's lifestyle and nutrition.
In the treatment of the disease, drugs are used simultaneously to affect different links in pathogenesis.
Main directions of treatment:
- Eliminate causal microorganisms.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy.
- Normalization of blood circulation in the prostate and pelvic organs.
- Normalization of prostatic toxins with adequate drainage.
- Normalization of hormone profiles.
- Prevent organ sclerosis.
To treat chronic prostatitis, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Antibacterial.
- Anticholinergic.
- Vasodilator.
- alpha1- adren - cover.
- Inhibitor of 5α reductase.
- Cytokine inhibitors.
- NSAIDs.
- Vascular protectant.
- Immunomodulators.
- Drugs that affect uric acid metabolism.
Antibiotics for bacterial chronic prostatitis
Antimicrobial therapy should take into account the antibiotic susceptibility of the identified microorganisms.If the causative agent is not identified, empiric antimicrobial therapy is used.
The drugs of choice are second to fourth generation fluoroquinolones.They penetrate rapidly into glandular tissue by conventional application methods and are active against a wide range of Gram-negative microorganisms as well as Ureaplasma and Chlamydia.If antimicrobial therapy fails, the following factors should be considered:
- Multiple resistance of microbiota,
- Short-term (less than 4 weeks) treatment,
- The wrong choice of antibiotics and their dosage,
- Changes in pathogen type,
- There are bacteria living in the prostate duct, which is covered with a protective outer membrane.
The duration of treatment should be at least 4 weeks, followed by mandatory bacteriological control.If bacteriuria remains in the third part of the urine and the prostate secretion exceeds 103The course of repeated antibacterial therapy for CFU/ml is specified for 2 to 4 weeks.
Cytokine inhibitors for the treatment of chronic prostatitis
Cytokines are glycoproteins secreted by immune cells and other cells under conditions of inflammation and immune responses.They actively participate in the development of chronic inflammatory processes.
NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have anti-inflammatory properties and can reduce pain and fever.It is widely used in the form of tablets and suppositories to treat chronic prostatitis.The most effective route of administration is rectal.
Immunotherapy
In the treatment of bacterial chronic prostatitis, immunomodulators are used in addition to antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.The most effective route of rectal administration is.Immunomodulators are widely used to increase the functional activity of phagocytic cells and help eliminate pathogens more effectively.
Alpha-blockers in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
Alpha-1 adrenergic blockers have been shown to normalize smooth muscle tone in the prostatic urethra, seminal vesicles, and prostatic vesicles, making this group of drugs very effective in treating this disease.Alpha-1 adrenergic blockers are used to treat patients with severe voiding disorders in the absence of an active inflammatory process.
For CPPS, the treatment period ranges from 1 to 6 months.
5a-Reductase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Nonbacterial Prostatitis and CPPS
It has been established that, under the influence of 5a-reductase, testosterone is converted into the prostatic form of 5a-dihydrotestosterone, the activity of which in prostate cells is more than 5 times greater than that of testosterone itself, which in the elderly leads to organ enlargement due to epithelial and stromal components.
When taking 5a-reductase inhibitors, atrophy of interstitial tissue was observed for 3 months, atrophy of glandular tissue was observed for 6 months, secretory function was suppressed, pain severity and gland volume were reduced, and organ tone and swelling were reduced.
The role of antisclerotic drugs in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
With prolonged inflammation of the prostate, fibrosis develops, manifesting as microcirculation and urodynamic disorders.To prevent the fibrotic process, anti-sclerotic drugs are used.
Other drugs used to treat chronic prostatitis
In addition to the above-mentioned drugs, the following drugs are also used to treat the disease:
- Antihistamines.
- Vasodilator and vascular protective agent.
- Immunosuppressants.
- Drugs affecting urate metabolism and trisodium citrate.
Herbal products
Effectively treat prostatitis, the drug is used in the form of candles containing a complex of bioactive peptides isolated from the prostate of a bovine.
Under the influence of the drug:
- Stimulates metabolic processes in glandular tissue.
- Improve microcirculation.
- Reduces edema, leukocyte infiltration, stagnation and pain.
- Prevent thrombosis in the prostate venous.
- Increases activity of irritant secretory epithelium.
- Improvement of sexual function (increased libido, restoration of erectile function and normalization of spermatogenesis).
Prostate finger massage
Many researchers say that in chronic prostatitis, known contraindications should be considered and finger massage should be used.
physiotherapy
The effectiveness of physical therapy procedures in the treatment of prostatitis has not been proven today, the mechanism of action has not been scientifically determined, and adverse effects have not been studied.
Prevent chronic prostatitis
To start preventing the development of chronic prostatitis, you should know:
- Over the years, the risk of developing the disease increases.
- Representatives of black races are more susceptible to the disease.
- Family predisposition to the disease cannot be ruled out.
People who tend to develop chronic prostatitis should pay more attention to their health.
Disease prevention tips:
- Take a sufficient amount of liquid.Frequent urination can promote leaching bacteria in the urethra.
- Prevent diarrhea and constipation.
- Abide by a rational diet.Do not eat foods saturated with carbohydrates and saturated fats, as this can lead to weight gain.
- It should be limited to substances that stimulate the urethra: fresh and spicy dishes, smoked meat, seasonings and seasonings, coffee and alcohol.
- Refuse to smoke.Nicotine has a negative impact on the condition of the blood vessel wall.
- Don't get too cold.
- Do not hold the emptying of the bladder.
- Live an active lifestyle and play sports.Performing exercises to strengthen the muscles of the pelvis allows you to eliminate stagnation of venous blood, thus supporting the normal function of the prostate.
- Outdated sex life.Avoid long-term abstinence.Iron should be released from the secret in time.
- Monogamous believers.Illegal sexual relations increase the likelihood of obtaining sexually transmitted diseases.
- If a complaint occurs in the urinary genital authorities, please contact your urologist immediately.